normal end tidal co2 levels
As a result oxygen from the alveolus where Po 2 is about 100 mm Hg diffuses into the blood and CO 2 diffuses from the blood into the alveolus where Pco 2 measures about 40 mm. What Is A Normal End-tidal Co2.

Figure 1 From Applications Of End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Etco2 Monitoring In Emergency Department A Narrative Review Semantic Scholar
For a person with normal lungs the difference between end tidal and Paco2 can vary between 5-8mmHg depending on the book your reading.

. The normal values are 5-6 CO2 which is equivalent to 35-45 mmHg. End-tidal carbon dioxide ETCO2 is the level of carbon dioxide that is released at the end of an exhaled breath. End-tidal capnography or end-tidal CO2 EtCO2 monitoring is a non-invasive technique that measures the partial pressure or maximal concentration of carbon dioxide CO2 at the end of an exhaled breath.
Levels of end-tidal carbon dioxide are low despite normal respiratory rate in individuals with long COVID J Breath Res. In thromboembolism ETCO2 is significantly lower than normal due to the reduction of pulmonary perfusion and increased alveolar dead space that reduces the amount of CO2 exhaled from the lungs so venous carbon dioxide pressure PvCO2 increases and all of these changes lead to an increase in arterial CO2-ETCO2 gradient. The normal values are 5 to 6 CO2 which is equivalent to 35-45 mmHg.
According to the book by Hockenberry and Wilson 2015 p 1140 normal values of ETCO2 are 30-43 mmHg which is slightly lower than arterial PaCO2 35-45mmHg. Levels of end-tidal carbon dioxide are low despite normal respiratory rate in individuals with long COVID. Monitoring of end-tidal carbon dioxide EtCO2 is a noninvasive method that measures the partial pressure or maximal concentration of carbon dioxide CO2 at the end of exhaled breath which is expressed as a percentage of CO2.
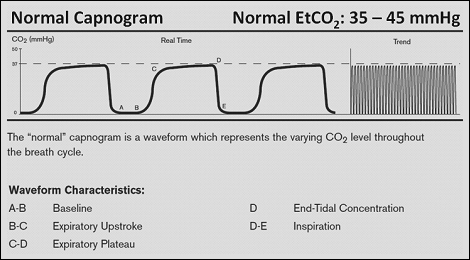
End-tidal capnography or end-tidal CO2 EtCO2 monitoring is a non-invasive technique that measures the partial pressure or maximal concentration of carbon dioxide CO2 at the end of an exhaled breath. Continuous Waveform Capnograpy is written as PETCO2 which stands for patient end-tidal carbon dioxide. End tidal CO 2 monitoring is represented as a number and a graph on a monitor.
In conditions of normal breathing 6 Lmin 12 breathsmin 500 ml for tidal volume etCO 2 is very close to alveolar CO2. The height of the ETCO2 waveform during CPR has been used as an indirect measure of adequate chest compressions helping those involved in resuscitation monitor the effectiveness of their compressions in real time. 78 Nitrogen 21 Oxygen 1 CO2 and other gases Exhaled gases.
In normal conditions CO2 is 5 to 6 which is equivalent to 35-45 mmHg. Utility of end-tidal carbon dioxide detector during stabilization and transport of critically ill children. The normal values are 5 to 6 CO2 which is equivalent to 35-45 mmHg.
End-tidal CO2 EtCO2 monitoring is a noninvasive technique which measures the partial pressure or maximal concentration of carbon dioxide CO2 at the end of an exhaled breath which is expressed as a percentage of CO2 or mmHg. 35-40 mm Hg PETCO2 less than 10 indicates ineffective chest compressions. In the awake adult normal cardiac index lies between 25-4 Lminm2 with an ETCO2 of 35-45 mmHg.
ETCO2 levels reflect the adequacy with which carbon dioxide CO2 is carried in the blood back to the lungs and exhaled. The normal values are 5 to 6 CO2 which is equivalent to 35-45 mmHg. Measuring End Tidal CO2 Daltons Law.
MmHg Relate to the air we breath. The amount of CO2 at the end of exhalation or end-tidal CO2 ETCO2 is normally 35-45 mm HG. When CO2 diffuses out of the lungs into the exhaled air a device called a capnometer.
So the short answer is you are right about the ranges 35-45 but that is for actual PaCo2 drawn from an ABG. Total pressure of a gas is the sum of the partial pressures of the gas Expired CO2 measured PetCO2 mmHg in waveform Percentage Normal Levels PaO2 85-100mmHg PaCO2 35-45mmHg Percentage vs. In normal conditions CO2 is 5 to 6 which is equivalent to 35-45 mmHg.
The number is called capnometry which is the partial pressure of CO 2 detected at the end of exhalation ranging between 35 - 45 mm Hg or 40 57 kPa. Carbon dioxide is produced in the body as a by-product of metabolism and is eliminated by exhaling. End-tidal CO2 EtCO2 monitoring is a noninvasive technique which measures the partial pressure or maximal concentration of carbon dioxide CO2 at the end of an exhaled breath which is expressed as a percentage of CO2 or mmHg.
Accuracy of end-tidal PCO2 measurements using a sidestream capnometer in infants and children ventilated with the Sechrist infant ventilator. The amount of CO2 at the end of exhalation or end-tidal CO2 ETCO2 is normally 35-45 mm HG. Monitoring of end-tidal carbon dioxide EtCO2 is a noninvasive method that measures the partial pressure or maximal concentration of carbon dioxide CO2 at the end of exhaled breath which is expressed as a percentage of CO2.
2 to near normal normal EtCO 2 35-45 mmHg represents marked increase of CO 2 delivery to lungs suggesting ROSC If patient develops an organized rhythm after VFVTasystole check EtCO 2 to see if ROSC has occurred CONFIRM PLACEMENT OF ETT After intubation if ETCO 2 10mm Hg tube in trachea. End-tidal CO2 EtCO2 monitoring is a noninvasive technique which measures the partial pressure or maximal concentration of carbon dioxide CO2 at the end of an exhaled breath which is expressed as a percentage of CO2 or mmHg. In the pulmonary artery deoxygenated blood has a partial pressure of carbon dioxide Pco 2 of approximately 46 mm Hg and a partial pressure of oxygen Po 2 of roughly 40 mm Hg.
Since problems with lungs are not common and gas exchange between alveoli and the blood is swift and effective alveolar CO 2 reflects arterial CO 2. The waveform is called capnograph and shows how much CO 2 is present at each phase of the respiratory cycle. 21 Hillier SC Badgwell JM Mcleod ME Creighton RE Lerman J.
For a person with normal lungs the difference between end tidal and Paco2 can vary between 5-8mmHg depending on the book your reading.
The Normal Capnograph Waveform Deranged Physiology

Exhaled Carbon Monoxide End Tidal Co2 And Peripheral Oxygen Saturation Download Table

How To Read And Interpret End Tidal Capnography Waveforms Emsuk Learning

How To Read And Interpret End Tidal Capnography Waveforms Emsuk Learning

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

End Tidal Capnography Can Be Useful For Detecting Diabetic Ketoacidosis Monitoring Copd Acep Now

Average Etco2 Kpa During Cpr In Patients With Or Without Rosc Download Scientific Diagram

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project
End Tidal Co2 Monitoring In The Pre Hospital Environment More Than Just Endotracheal Tube Placement Confirmation Journal Of Paramedic Practice

Normal And Abnormal Capnography Waveforms Infographic Capnoacademy Capnoacademy

The Impact Of Ventilation Rate On End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Level During Manual Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Resuscitation

Capnography Provides Bigger Physiological Picture To Maximize Patient Care Jems Ems Emergency Medical Services Training Paramedic Emt News

Exhaled Carbon Monoxide End Tidal Co2 And Peripheral Oxygen Saturation Download Table
Capnogram R Series Defibrillator Zoll Medical Uk
Riding The Wave Of Capnography Understanding Etco2 Vetbloom Blog
Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Educationcapnography In The Ed Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Education

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

